Disclosure
This website is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
DIY car interior disassembly is the process of carefully taking apart your vehicle’s cabin components. It is a crucial skill for deep cleaning, repairs, or custom upgrades. This guide provides the expert knowledge to do it safely and correctly.
Proper disassembly prevents costly damage to fragile clips, panels, and electrical connections. Our complete guide eliminates the guesswork. You will learn proven methods to avoid common, expensive mistakes.
Best Tools for DIY Car Interior Disassembly
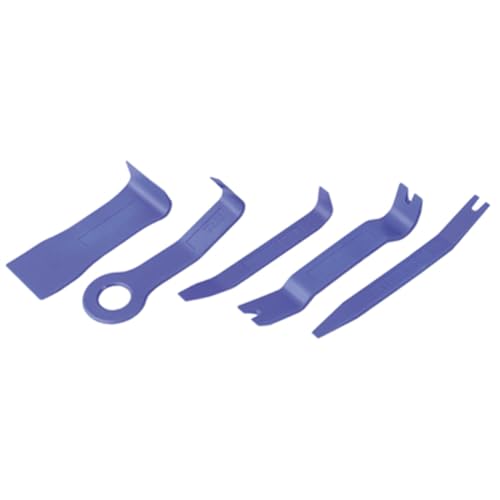
OTC 4489 Trim Fastener and Molding Removal Set – Best Overall Kit
This comprehensive set is the ideal starter kit for any disassembly project. It includes nylon pry tools in various shapes to safely remove clips and panels without scratching delicate surfaces. The durable construction handles significant prying force, making it the most recommended option for beginners and pros alike.
- Tools are made of plastic to prevent damage to trim, moldings, alloy wheels…
- Can be used on trim fasteners and moldings inside, or outside the vehicle
- OTC 4489 Trim Fastener and Molding Removal Set
GLK Auto Trim Removal Tool Set – Best for Door Panels
Specifically designed for stubborn door panel clips, this tool is a must-have for efficient removal. Its forked ends slide behind panels to cleanly release plastic retainers. The ergonomic handles provide superior leverage, preventing broken clips and saving you money on replacement parts during your interior teardown.
- Stronge : Trim Removal Tool Made with NEWEST strong Nylon Plastic Material,…
- Safe: The Auto Trim Removal Tool Set Will Not Mar Surfaces Like Metal…
- Effective:The Plastic Pry Tool Kit with Different Design can Easily Remove…
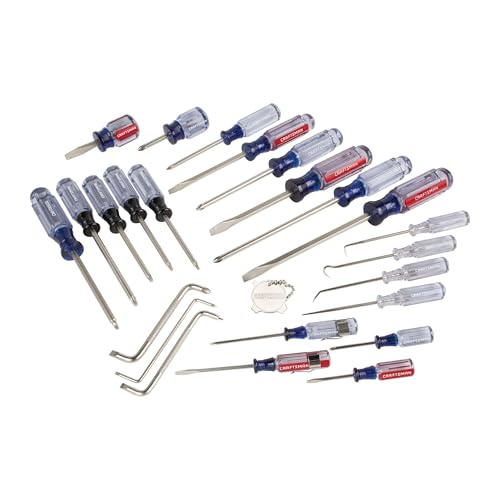
CRAFTSMAN 25-Piece Screwdriver Set – Essential for Fasteners
Car interiors use a variety of screw heads. This set provides precise bits for Torx, Phillips, and flat-head screws commonly found in consoles and trim. The magnetic tip and comfortable grip allow for easy access in tight spaces, ensuring you have the right driver for every fastener you encounter.
- Alloy-steel blades are heat-treated for strength and durability
- Coated with a satin-nickel finish
- Comfort Optimized handle for high and low torque applications
Essential Safety and Preparation Steps Before You Begin
Proper preparation is the most critical phase of any car interior disassembly project. Rushing in can lead to broken parts, electrical shorts, or personal injury. Taking these initial steps ensures a smooth, safe, and successful process from start to finish.
Gathering Your Tools and Creating a Workspace
Before touching a single panel, assemble all necessary tools and prepare your vehicle. This prevents mid-project frustration and protects your car’s interior from accidental damage.
- Disconnect the Battery: Always disconnect the negative terminal first. This prevents airbag deployment and protects the vehicle’s electrical system from shorts.
- Organize Hardware: Use small containers or a segmented tray to store screws, bolts, and clips. Label them by location (e.g., “driver door,” “center console”).
- Protect Surfaces: Lay a soft blanket over fenders and doors to prevent scratches. Use interior protectant on plastic panels to avoid scuffs from tools.
Common Fastener Types and Removal Techniques
Car interiors are held together by a variety of fasteners. Using the wrong technique is the leading cause of broken plastic parts. Identify these common types before applying force.
| Fastener Type | Identification | Proper Removal Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Plastic Push Clips | Round pins with a central expanding pin | Trim removal tool or flathead screwdriver (with cloth) |
| Christmas Tree Clips | Fir tree-shaped with ribbed sides | Wide, flat trim tool to pry evenly from base |
| J-Nut or U-Clip | Metal clip that a bolt screws into | Remove the bolt; the clip stays on the panel |
| Torx or Star Head Screws | Star-shaped recess in screw head | Correct size Torx bit (e.g., T15, T20, T25) |
Apply steady, even pressure when prying. If something feels stuck, stop and look for a hidden screw or clip. Patience here saves money and time on replacements.
Key Takeaway: Never force a component. Always disconnect the battery first, organize all hardware, and identify the fastener type before attempting removal. This methodical approach prevents the vast majority of DIY disassembly mistakes.
Step-by-Step Guide to Removing Common Interior Components
This section provides a detailed, component-specific breakdown of the disassembly process. Following these proven methods will help you safely remove major interior pieces without causing damage.
How to Remove a Car Door Panel Safely
Door panel removal is a frequent task for speaker upgrades or window regulator repairs. The process is similar across most modern vehicles. Always work from the bottom edges upward to avoid breaking plastic tabs.
- Locate and Remove Visible Screws: Check the door pull cup, armrest, and behind reflector lights. Use the correct screwdriver bit for each.
- Release the Plastic Clips: Insert a trim tool between the panel and door metal near the bottom. Gently pry to pop the first clip, then work around the perimeter.
- Disconnect Electrical Connectors: Once the panel is loose, carefully tilt it away. Unplug the wiring harness for the power window switch, speakers, and door lights.
- Lift the Panel Up and Off: Most panels hook over the top edge of the door frame. Lift the panel straight upward to release it from this hook.
Front Seat Removal Process and Precautions
Removing seats is necessary for deep cleaning or full carpet replacement. It involves heavy components and critical safety systems, so caution is paramount.
- Disable Airbag System: Ensure the battery has been disconnected for at least 15 minutes before starting. This allows the airbag system’s backup capacitor to discharge.
- Locate Seat Bolts: Typically four bolts (one at each corner) secure the seat to the floor. They are often Torx bolts (e.g., T50) and can be very tight.
- Handle Wiring with Care: After unbolting, slide the seat back to access the large electrical connector under it. Press the tab and disconnect it to free the seat.
Pro Tip: When removing any component, take clear photos with your phone at each step. These photos are an invaluable reference for reassembly, ensuring every clip and wire goes back in the correct place.
Advanced Techniques and Troubleshooting Common Problems
Once you master basic removal, you may encounter stubborn components or complex assemblies. This section covers advanced techniques for tricky situations and solutions for the most frequent issues DIYers face. These tips can prevent project-stopping frustrations.
Dealing with Stuck or Broken Plastic Clips and Fasteners
Plastic clips can become brittle with age and temperature cycles. Forcing them is a recipe for breakage. Use these methods to handle problematic fasteners effectively and minimize damage.
- For Stuck Push Clips: Spray a small amount of silicone-based lubricant around the clip’s base. Let it penetrate for a minute, then gently twist the trim tool while prying.
- If a Clip Breaks: Remove the broken pieces from both the panel and the mounting hole. Use needle-nose pliers to extract the center pin from the hole.
- Essential Replacement: Always keep a universal trim clip assortment kit on hand. These kits contain the most common clip sizes and styles for repairs.
Navigating Complex Dashboard and Center Console Removal
Dashboard disassembly is an advanced procedure often needed for heater core or stereo wiring access. It requires extreme patience and systematic organization due to the number of interconnected parts.
- Start with Obvious Components: Remove the radio/head unit, climate control knobs, and any trim pieces surrounding the dashboard. These usually hide critical screws.
- Work in Layers: The dashboard is a multi-layered assembly. Remove the lower knee panel first, then side trim, then the main dashboard cover. Document each layer with photos.
- Mind the Airbag and Sensors: Be acutely aware of airbag modules, often located in the dashboard. Do not disconnect yellow airbag connectors unless absolutely necessary and with the battery disconnected.
| Common Problem | Likely Cause | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Panel won’t budge after removing visible screws | Hidden screw or clip behind a label, switch, or small access plug | Inspect carefully for any removable badges or plugs. Gently pry with a fingernail first. |
| Electrical connector won’t release | Locking tab not fully disengaged or dirt/debris | Look for a locking lever or button. Press it firmly while pulling the connector apart. Never pull by the wires. |
| Stripped screw head | Using incorrect bit size or worn tool | Use a rubber band between the screw head and driver for grip. As a last resort, use a screw extractor kit. |
Reassembly Best Practices and Final Quality Checks
Proper reassembly is just as critical as careful disassembly. This final phase ensures your interior looks professional, functions correctly, and remains rattle-free. A methodical approach here guarantees your hard work pays off with flawless results.
Ensuring a Rattle-Free and Professional Reinstallation
The key to a quiet interior is secure connections and proper clip alignment. Rushing reassembly often leads to annoying noises and loose panels that require rework.
- Replace Worn Clips: Never reuse clips that are cracked, stretched, or missing their center pins. New clips ensure a tight, secure fit.
- Align Before Pressing: Hold the panel near its mounting position and visually align all clips with their corresponding holes. Apply even pressure across the panel to snap everything into place at once.
- Listen for the Click: Each plastic clip should make a distinct snapping sound when fully seated. If you don’t hear it, the clip is likely not engaged.
Post-Reassembly System Testing and Verification
Before considering the job complete, you must verify that all systems function correctly. This final testing protocol catches issues while components are still easily accessible.
- Reconnect the Battery: First, reconnect the negative terminal. Listen for any unusual sounds from electronic modules initializing.
- Test All Electrical Functions: Operate every switch and component you disconnected. Test power windows, door locks, seat adjustments, stereo, and all dashboard lights.
- Conduct a Visual and Physical Inspection: Look for uneven panel gaps or misalignment. Gently press on reassembled areas to check for movement or creaking sounds.
Final Checklist: Before driving, confirm: 1) All warning lights on the dash are off, 2) Airbag light follows its normal cycle and turns off, 3) No tools or loose parts are left inside the vehicle, and 4) All seat belts latch and retract properly.
If a system fails, recheck the relevant electrical connectors first. They may be loose, dirty, or not fully locked. Addressing issues now prevents more complicated diagnostics later.
Vehicle-Specific Considerations and Finding Technical Resources
While general principles apply, every vehicle make and model has unique quirks. This section guides you on how to access the precise information you need for your specific car. Using the right resources is the difference between guessing and knowing.
How to Locate a Service Manual for Your Exact Car Model
A factory service manual (FSM) or a reputable aftermarket equivalent is the ultimate resource. It provides exploded diagrams, torque specifications, and exact procedures. Never rely on generic guides for safety-critical components.
- Factory Service Manuals (FSM): Published by the vehicle manufacturer, these are the most accurate. Search online for “[Your Car Year/Make/Model] factory service manual PDF.”
- Reputable Aftermarket Manuals: Brands like Haynes and Chilton offer model-specific manuals. They combine clear photos with step-by-step instructions tailored to your vehicle.
- Official Dealer Repair Systems: Some manufacturers sell short-term subscriptions to their online technical portals (e.g., Honda Service Express, Subaru STIS).
Leveraging Online Forums and Video Tutorials Effectively
The DIY community is an invaluable asset. Model-specific forums and video platforms host a wealth of shared knowledge from other enthusiasts who have done the exact job.
| Resource Type | Best Use Case | Key Tip for Success |
|---|---|---|
| Model-Specific Forums | Finding solutions to uncommon problems or accessing shared PDF guides. | Use the forum’s search function with specific keywords like “door panel removal” before posting a new question. |
| YouTube Video Tutorials | Visualizing the disassembly sequence and seeing tool angles on your exact model. | Watch the entire video first. Pause and replicate each step, don’t just follow along in real-time. |
| Digital Parts Catalogs | Identifying the official part number for broken clips or trim pieces. | Sites like partsouq.com or your dealer’s parts site use your VIN to show exploded diagrams with numbered parts. |
Pro Advice: Cross-reference your information. If a forum post suggests a method, try to verify it with a snippet from a service manual or a second video. This due diligence helps you follow the most reliable procedure.
Cost Analysis: DIY vs. Professional Interior Disassembly
Understanding the financial implications helps you decide when to tackle a project yourself and when to call a professional. This cost-benefit analysis goes beyond just parts and labor. It includes the value of your time, risk, and the potential for learning.
Breaking Down the Potential Savings of a DIY Approach
For non-critical projects like deep cleaning or basic upgrades, DIY offers significant savings. The primary costs are tools and replacement clips, which are minimal compared to shop labor rates.
- Labor Cost Avoidance: Professional shops typically charge $80-$150 per hour. A multi-hour disassembly job for carpet replacement or sound deadening can save you hundreds.
- Investment in Reusable Tools: A $50-100 investment in a quality trim tool set and screwdrivers pays for itself in the first project and lasts for years.
- Control Over Parts Quality: You choose the exact replacement clips or upgraded components, avoiding potential markup on parts from a shop.
When to Hire a Professional: Recognizing Complex Jobs
Certain scenarios carry high risks or require specialized tools and knowledge. In these cases, paying for professional service is the smarter, safer financial decision.
| Situation | DIY Risk | Professional Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Airbag System Components | Risk of accidental deployment causing injury or costly system repair. | Technicians have scan tools to safely disable/enable the system and proper training. |
| Integrated HVAC/Heater Core Work | Extremely complex dash removal; risk of damaging expensive climate control modules. | Experience with the specific model’s assembly and specialized tools for refrigerant handling. |
| Modern Integrated Infotainment Systems | Complex wiring and coding; may require proprietary software to recalibrate after reconnection. | Access to manufacturer-level diagnostic software and programming capabilities. |
Rule of Thumb: If the job involves the vehicle’s safety systems (airbags, seat belt pre-tensioners), advanced electronics, or refrigerant lines, professional help is strongly recommended. For aesthetic, cleaning, or basic mechanical projects, DIY is highly feasible and cost-effective.
Maintaining Your Car’s Interior After Disassembly and Reassembly
After successfully completing your project, proper maintenance ensures your interior stays in top condition. The work you’ve done can even make future cleaning and upkeep easier.
Post-Project Cleaning and Care for Exposed Areas
Disassembly often reveals hidden dirt and dust. Use this opportunity to thoroughly clean areas normally inaccessible. This deep clean improves air quality and prevents future wear.
- Vacuum and Wipe Down: Before reassembling everything, vacuum the exposed floor, door cavities, and behind panels. Wipe metal and plastic surfaces with a damp microfiber cloth.
- Inspect for Moisture or Corrosion: Look for signs of water leaks, especially in door bottoms and footwells. Address any leaks now to prevent mold and electrical issues.
- Apply Protectants: Once clean, apply a UV-protectant to plastic and vinyl surfaces you’ve accessed. This helps prevent fading and cracking from sun exposure.
Long-Term Tips to Preserve Trim and Fasteners
Plastic becomes brittle over time due to heat cycles and UV exposure. Proactive care extends the life of clips and panels, making any future disassembly much smoother.
- Lubricate Plastic Tracks and Guides: Use a dry silicone lubricant on window channels, seat tracks, and any plastic sliding mechanisms you exposed. This reduces friction and wear.
- Keep a Clip Inventory: Note which clip types were most prone to breakage on your vehicle. Keep a small stock of these specific clips in your garage for quick future repairs.
- Periodic Check for Rattles: After a few weeks of driving, press on reassembled panels during your regular wash. If a new rattle develops, it likely indicates a clip that didn’t fully seat.
Maintenance Mindset: View disassembly not as a one-time task, but as an opportunity for preventative maintenance. Cleaning hidden areas and lubricating components during the process adds years of life to your car’s interior and ensures it remains pleasant and functional.
Conclusion: Mastering DIY Car Interior Disassembly with Confidence
You now possess the complete knowledge to safely take apart your car’s interior. This guide has covered essential tools, step-by-step techniques, and advanced troubleshooting. You can tackle projects from deep cleaning to component upgrades.
The key to success is methodical preparation and patience. Always disconnect the battery, organize hardware, and use the right tools for each fastener. Refer to vehicle-specific resources for complex tasks.
Start with a small project like a door panel to build your confidence. Apply these proven methods to save money and gain valuable skills. Your car’s interior is now an accessible space for improvement and repair.
You have the blueprint for professional results. Approach your next project with confidence and enjoy the satisfaction of a job done right.
Frequently Asked Questions about DIY Car Interior Disassembly
What is the most important safety step before starting interior disassembly?
Always disconnect your car battery before beginning any interior work. This is the single most critical safety precaution. It prevents accidental airbag deployment and protects sensitive electronic components from short circuits.
Disconnect the negative terminal first and secure it away from the battery post. Wait at least 15 minutes for the system’s backup power to drain before touching any components connected to airbag or seat belt systems.
How do I remove interior door panels without breaking the plastic clips?
Use a dedicated nylon trim removal tool, not a screwdriver. Start at the bottom corner of the panel and gently pry to release the first clip. Work your way around the perimeter, applying steady pressure directly behind each clip location.
Listen for a distinct “pop” as each clip releases. If a section feels stuck, stop and check for a hidden screw. Applying heat from a hairdryer to cold plastic can make clips more pliable and less likely to snap.
What should I do if I break a plastic clip during disassembly?
First, carefully remove all broken pieces from both the panel and the mounting hole using needle-nose pliers. Do not leave fragments behind, as they can cause rattles or prevent proper reinstallation of the new clip.
Universal automotive trim clip kits are inexpensive and widely available. They contain the most common sizes. Match the broken piece to a new one from the kit for a perfect, rattle-free replacement.
How can I find a service manual for my specific car model?
Search online for “[Your Year, Make, Model] factory service manual PDF.” Manufacturer manuals are the most accurate. Reputable aftermarket publishers like Haynes or Chilton also produce excellent model-specific guides with clear photos and instructions.
For digital resources, check model-specific enthusiast forums. Members often share helpful links. Some automakers also offer short-term subscriptions to their official online technical portals for detailed repair information.
What is the best way to organize screws and bolts during disassembly?
Use small magnetic trays, labeled plastic bags, or a compartmentalized organizer. Immediately place hardware into a container labeled for its specific component, such as “driver door” or “center console.” This simple habit is crucial for a smooth reassembly process.
Take a quick photo with your phone of each area before you remove hardware. This visual reference is invaluable if you forget where a particular screw belongs weeks later during reassembly.
Why does my dashboard have a warning light after reassembling my interior?
A warning light, especially the airbag light, often indicates an electrical connector was not fully reseated or was damaged. The most common cause is forgetting to reconnect a sensor or plugging it in incompletely.
First, double-check every electrical connection you touched. Ensure each connector is fully clicked into place. If the light persists, you may need a professional scan tool to read and clear the specific fault code from the vehicle’s computer.
When should I definitely hire a professional instead of attempting DIY disassembly?
Hire a professional for any job involving airbag components, seat belt pre-tensioners, or complex HVAC/heater core access. These systems carry high injury risk or require specialized tools and knowledge for proper handling and recalibration.
If a procedure requires discharging the air conditioning system or proprietary diagnostic software to reprogram modules, the cost of professional tools and training makes hiring a technician the more practical and safer choice.